- Removable Partial Dentures
- Tooth Extraction: Post-Operative Instructions
- Your Wisdom Teeth
- Taking Care of Your Teeth and Gums
- Basic Flossing
- Do You Have a Cracked Tooth?
- Periodontal Disease: Your Complete Guide
- Basic Brushing
- Periodontal Disease: Keep Your Gums Healthy
- Fluoride: Nature's Cavity Fighter
- Hate To Floss? 3 Other Ways to Clean Between Your Teeth
- Handling Your Child's Dental Emergency
- Get the Facts about Mouth and Throat Cancer
- Oral Health and the HPV Vaccine
- Do You Grind Your Teeth?
- Tooth Decay in Baby Teeth
- Do You Have Sleep Apnea?
- Your Single Tooth Implant
- Your Child's Teeth
- Tobacco and Oral Health
- Seal Out Decay
- Temporomandibular Disorders (TMD)
- Healthy Smiles for Mother and Baby
- Healthy Mouth, Healthy Body: Making the Connection
- Baby Teeth: When They Come In, When They Fall Out
- Thumb Sucking, Finger Sucking and Pacifier Use
- Sip and Snack All Day? Risk Decay!
- 3 Tooth Replacement Options
- Tooth Erosion
- Tooth Decay
- Treating Cavities
- Should You Take Antibiotics before Your Dental Treatment?
- Mouthguards and Sports Safety
- Gum Recession Causes and Treatments
- Dental X-Ray Exams
- Diabetes and Your Oral Health
- Scaling and Root Planing
- Pregnancy and Oral Health
- Your Dentures
- Your Child's First Visit to the Dentist
- Root Canal Therapy Can Save Your Tooth
- Periodontal Disease - Don't wait until it hurts
- Why Do I Need a Bridge?
- Why Do I Need a Crown?
- Your Smile - An Owner's Manual
- Dental Sealants Protecting teeth, preventing decay
- Happiness is a Healthy Smile
- Dental Veneers - Improve Your Smile
- Tooth Whitening for a Brighter Smile
- Why Baby Teeth Are Important
- Dry Mouth
- Sealant Quick Reference
- Caries en Dientes de Leche
- Why Doesn't My Insurance Pay for This?
- Periodontal Maintenance: Stay on Top of Gum Disease
- Flossing Quick Reference
- Brushing Quick Reference
- Your Child's Teeth: Ages 6–12
- Your Child's Teeth: From Birth to Age 6
- Dental Implants: Are they an option for you
- Mouth Sores and Spots
- Sipping, Snacking and Decay
- Improving Your Smile
- Your Child's First Dental Visit
Did You Know That Your Dentist Can Check for Signs of Cancer at Every Visit?
Mouth and throat cancers can be deadly diseases. As recently as 2019, there were 53,000 new cases of mouth and throat cancer diagnosed and about 10,000 deaths from these cancers. Men are more than twice as likely to develop mouth and throat cancers as women.
Finding cancer early is important. Treatment may be more successful with mouth and throat cancers that are found early. Your dentist can check for these cancers every time you visit, so this is one more reason to see your dentist regularly.
This page will tell you some ways to lower your risk for mouth and throat cancer. By watching for the signs and symptoms listed here, you are more likely to find the cancer earlier if you do have it.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms?
Check your mouth in the mirror each day when you brush and floss. If there are any changes in your mouth or neck, or if you notice any of these signs or symptoms, contact your dentist.
Signs and symptoms of mouth cancer:
- A sore or irritation that doesn’t go away
- Red or white patches
- Pain, tenderness, or numbness in mouth, jaw, or lips
- A lump, thickening, rough spot, crust, or small eroded area
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing, speaking, or moving your jaw or tongue
- A change in the way your teeth or dentures fit together
- Loosening of the teeth
Be aware of any changes in your mouth or throat.
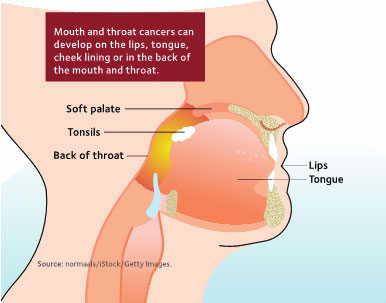
Additional Signs and Symptoms of Throat Cancer Include:
- Lump or growth in the throat or neck area
- Cough or sore throat that doesn’t go away
- Hoarseness or other changes in your voice
Am I at Risk for Mouth or Throat Cancer?
Anyone can get cancer. There are some factors that you can control—such as using any form of tobacco or heavy alcohol consumption—which increase your risk of getting mouth or throat cancer. Below is more information about factors that can affect your chance of developing these cancers.
- Tobacco and heavy alcohol use are two of the biggest risk factors. Tobacco use includes cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and smokeless tobacco like chew or dip.
- People who use tobacco products and drink alcohol have a greater chance of developing mouth or throat cancer than if they only did one or the other.
- Infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) can cause some forms of cancer in the back of the mouth or throat. HPV is very common and many people are not even aware that they have been infected.
- Spending long periods of time in the sun increases your risk of developing lip cancer.
- The risk of mouth and throat cancer increases with age. Though not always the case, it can occur more often in people over the age of 50.
How Can I Lower My Risk for Mouth and Throat Cancer?
- As part of your oral hygiene routine, watch for changes in the soft tissues of your mouth.
- Avoid all tobacco products, including cigarettes and chewing tobacco.
- Avoid heavy alcohol use.
- Talk to your physician or dentist about the HPV vaccine, especially for pre-teens aged 11 or 12.
- Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Visit your dentist for regular mouth and throat cancer check-ups.
When you quit using tobacco, your risk of developing mouth and throat cancers goes down.
How Can My Dentist Help?
During a dental exam, your dentist may check your face, neck, and mouth for lumps, red or white patches, and sore areas that do not heal. Your dentist can check for signs of mouth or throat cancers visually, manually, or with a combination of these methods.
Be sure to tell your dentist if you notice any changes in your mouth or neck. If signs of cancer are found early, treatment may be more successful. If you have any concerns about mouth and throat cancer, talk with your dentist. It may help save your life.
Visit Our Office
Office Hours
- MON8:30 am - 5:00 pm
- TUE8:30 am - 5:00 pm
- WEDClosed
- THUClosed
- FRI8:30 am - 5:00 pm
- SAT9:00 am - 2:00 pm
- SUNClosed